Foot conditions
Ingrown toenails
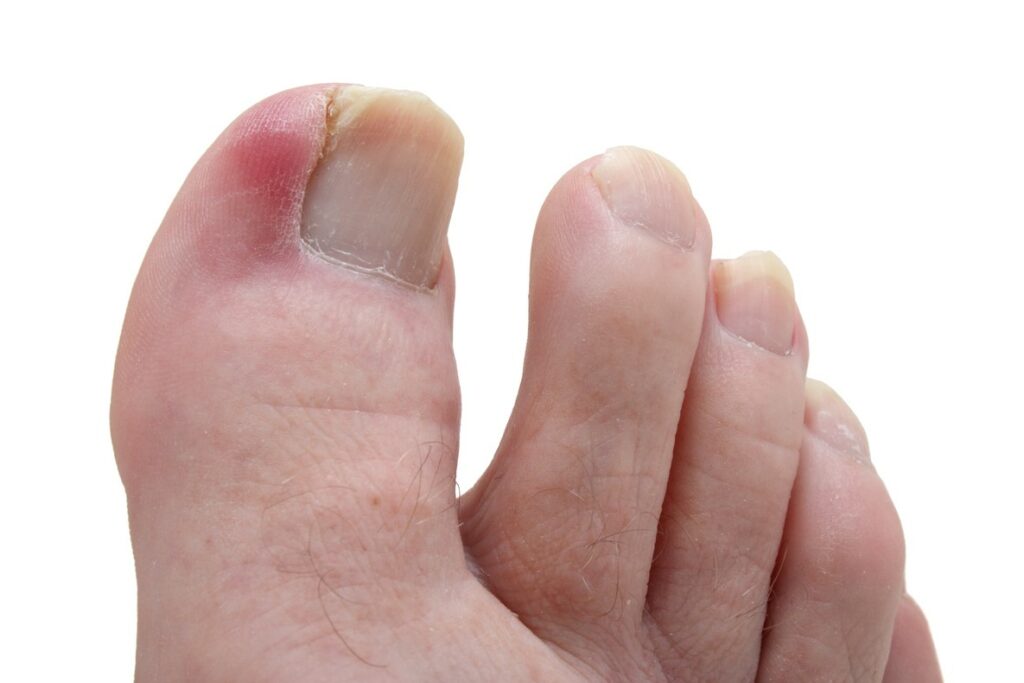
This is a condition when the nail curves and grows into the skin. Ingrown toenails are most commonly seen on the big toes, either on one or both sides of the toe, but can affect other toes as well. They often lead to pain and swelling and can cause infection if left untreated. It is therefore it is important to have them removed to relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
Hard skin and callus
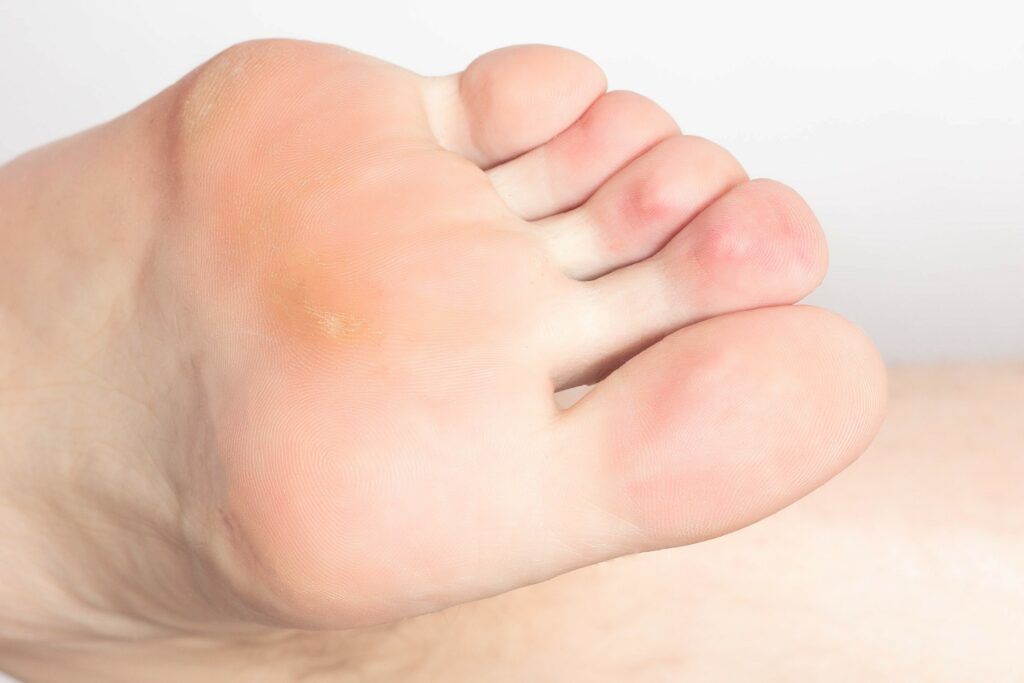
Hard skin is caused by repeated pressure and friction; as a result of everyday activities such as walking and running, but also things like poor fitting shoes and using work tools. Hardening of the skin is the body’s way of protecting against damage and a small amount is unlikely to cause problems. However, over time areas of hard skin can become more diffuse and thicken, developing into callus, causing tenderness and difficulty when walking. Hard skin and calluses can be effectively reduced through the use of scalpel parring and nail drills.
Corns
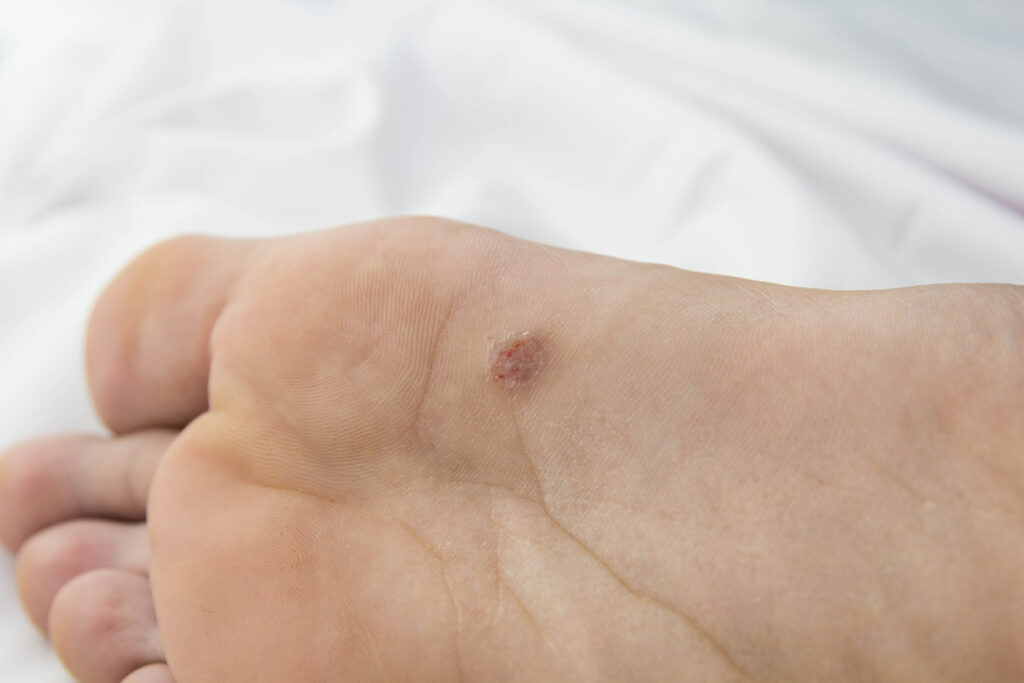
Hard corns are usually found where callus has already built up or on bony areas of the foot. Like a callus, a corn is created through a built up of hard dead skin, but is much smaller, with a hard centre shaped like an inverted cone. Corns can cause intense pain when pressed. They are treated by parring away the dead skin and removing its core.
You can also get other sorts of corns, such as soft corns which are usually white and rubbery and found in moist areas, such as in-between toes.
Verruca
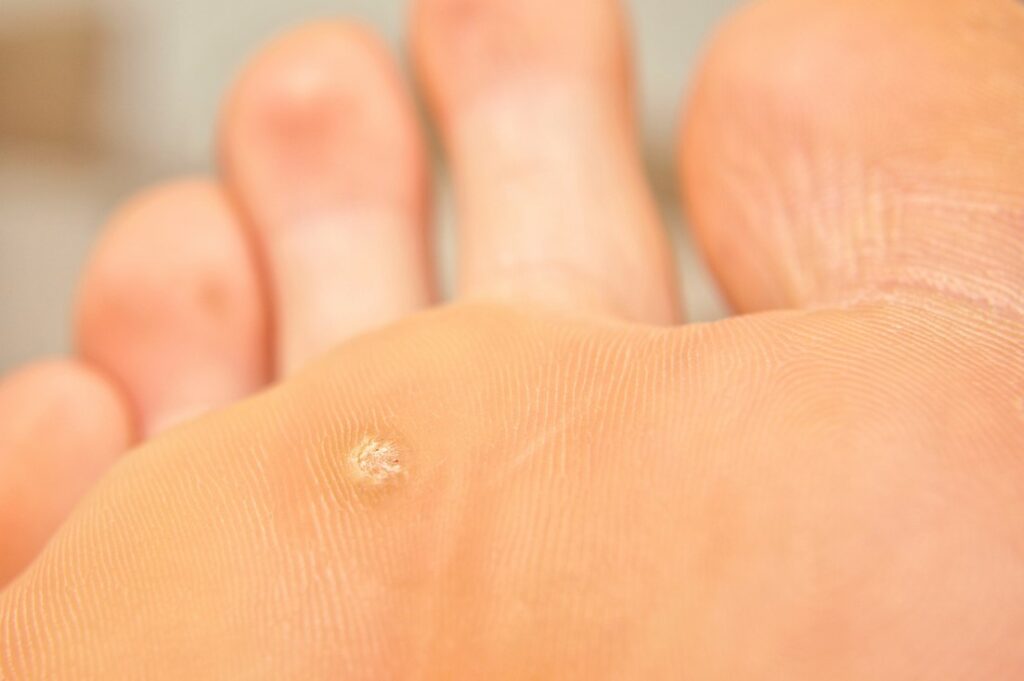
A verruca is a plantar wart that is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Most people will experience infection with HPV at some time in their life and verrucae is particularly common in children and adolescents. Verrucae are spread by contact, either directly from person to person or indirectly via surface contact, particularly if the skin is moist and in contact with roughened surfaces, for example in a communal swimming pool. A verruca will often clear on its own (unless you have a suppressed immune system), but can take months or even years. Therefore, if it causes you difficulty, or pain or you simply find it unsightly you may wish to seek treatment. There is no single treatment of a verruca that is 100% effective and therefore different types of treatment may be combined, such as zinc oxide tape and salicylic acid.
Athlete’s Foot
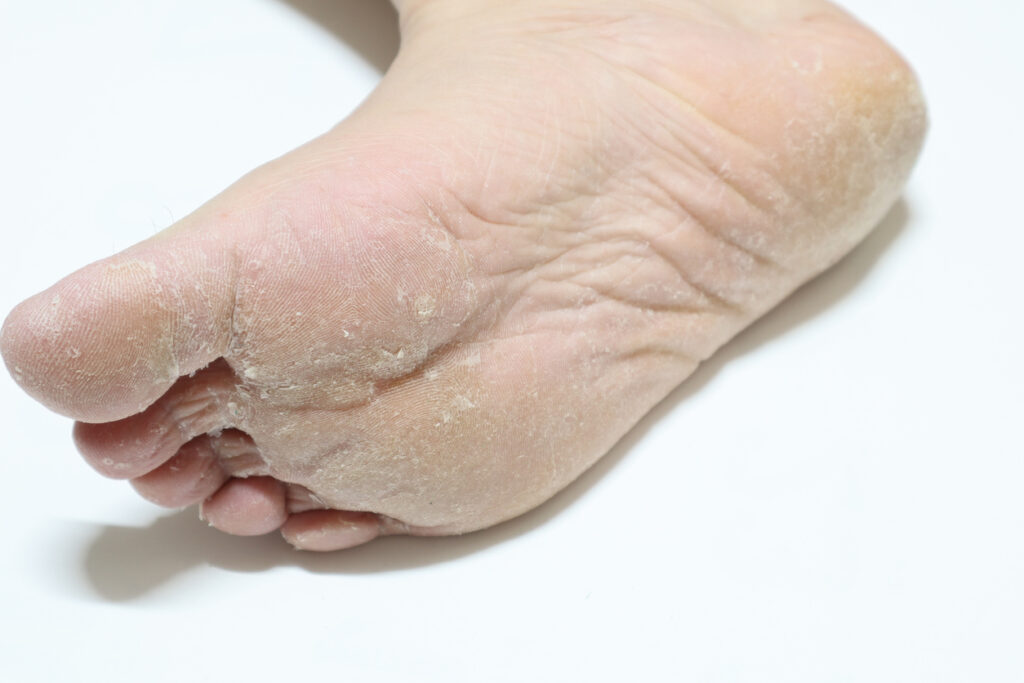
Also called Tinea Pedis, athlete’s foot is a common contagious fungal infection that effects the skin on the feet and is often found in-between toes, as well as on the soles and sides of your feet. Although not usually serious, it can cause itchiness and the skin to crack, making it susceptible to infection, particularly if you have a weakened immune system. If not treated if can spread to your toenails and cause fungal nail infections and therefore it is important to seek advice early.
Fungal nail infections
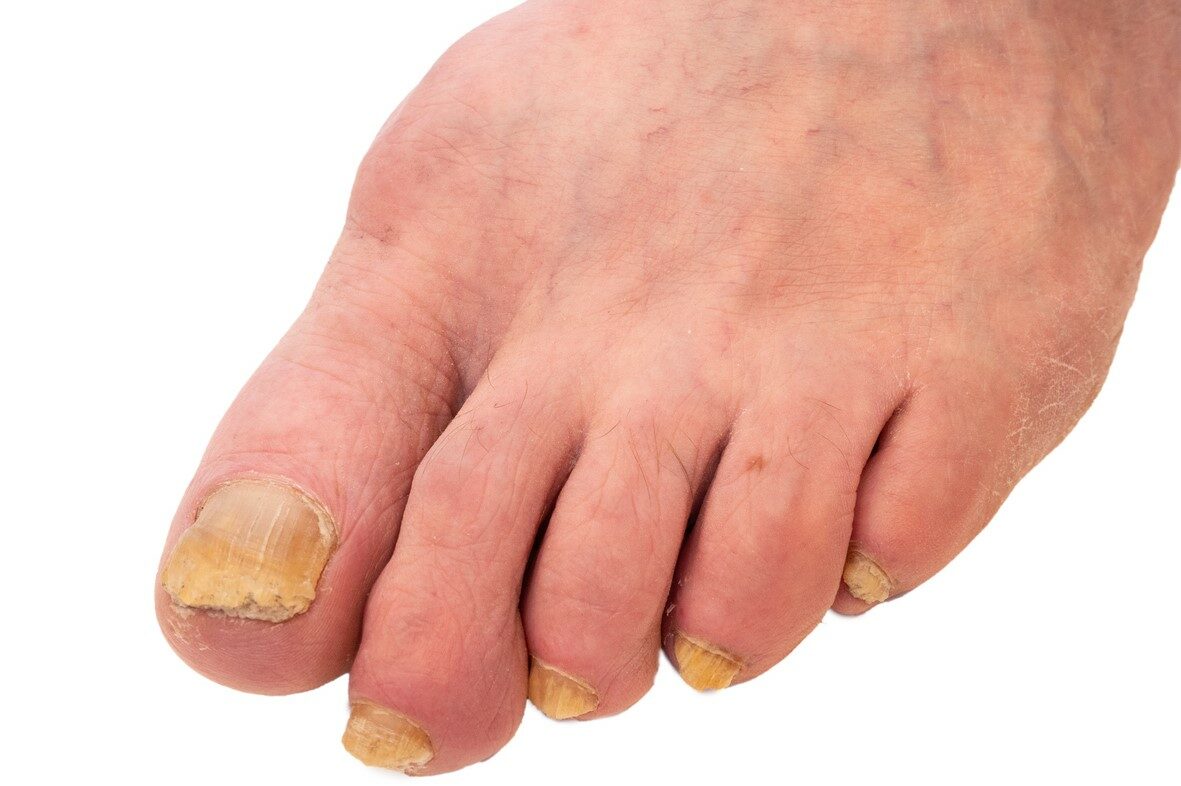
Fungal nail infections (medical term Onychomycosis) occur when spores of fungus make their way between your toenail and nail bed and feeds off the skin or the keratin in the nail. The infections can affect any part of your nail, including the plate, bed and root. It usually starts at the nail edge and spreads to the middle and sometimes effects the entire nail. As the infection spreads the nail changes colour, thickens and starts to crumble. The nail can become loose and separate from the nail bed itself and pain and may occur in the skin surrounding the nail.
The most commonly occurring fungi that infects the nail is called dermatophyte, which is also responsible for causing athlete’s foot. Less common are yeasts (eg. Candida) and moulds which do not cause athlete’s foot.
Being contagious, fungal infections can spread to other nails and in people with compromised immune systems, such as the elderly or people with diabetes, it can cause secondary bacterial infections, leading to serious complications such as ulcers.
Fungal nail infections can be difficult and slow to treat and in some cases may require a combination of both oral and topical medication. At Stride Out Footcare, we can thin your nails, which in addition to making thickened nails more comfortable, will allow topical medications to penetrate the nail easier.33.0%